The hippocampus is a brain structure belonging to the limbic system, located in the temporal lobe. It is crucial for many cognitive and emotional functions.
Location of the hippocampus
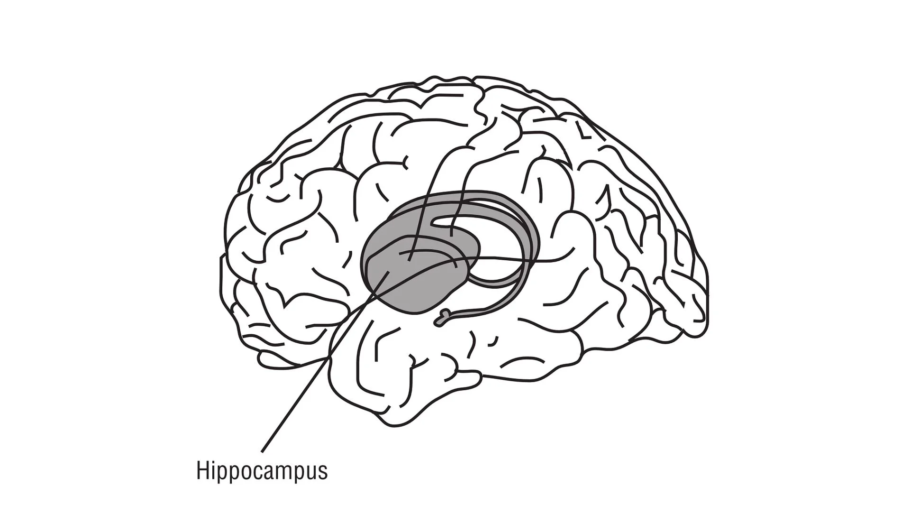
The hippocampus is located in the medial temporal lobe of the brain, deep inside the cerebral cortex, on either side of the brain. It is part of the limbic system, which is responsible for emotions, memory, and learning.
The hippocampus lies near the lateral ventricle of the brain, in its inferior part (temporal horn). It forms a structure resembling a curved tube, which is why its name comes from the Greek word hippokampos (“seahorse”). It is connected to other brain structures, such as the amygdala (emotions) and the entorhinal cortex (information processing).
Hippocampus functions
Memory and learning – the hippocampus plays a key role in memory consolidation, or transforming short-term memories into long-term ones. It is particularly important for declarative memory (facts, events).
Spatial navigation – helps with orientation in the field and creating cognitive maps of the environment. Damage to the hippocampus can lead to spatial disorientation.
Emotions – works with the amygdala to regulate emotions, especially in the context of processing memories with a strong emotional charge.
Neuronal plasticity – the hippocampus has the ability to neurogenesis, or create new neurons, which is important for brain adaptation and learning.
How to develop the hippocampus
The development and protection of the hippocampus are crucial for good memory, learning, and brain health. Here are some ways to support it:
Physical activity: regular exercise (e.g., running, swimming, yoga) increases neurogenesis in the hippocampus, improves circulation, and delivers oxygen to the brain.
A diet that includes:
- Omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, walnuts, flaxseed) – support neurogenesis,
- Antioxidants (berries, green tea, dark chocolate) – protect against oxidative stress,
- Curcumin (turmeric) – has neuroprotective effects,
- Flavonoids (cocoa, citrus fruits) – improve synaptic plasticity.
Mental training: learning new things (languages, playing an instrument, chess) activates the hippocampus. Reading, solving puzzles, and playing strategy games strengthen memory and cognitive functions.
Getting enough sleep: REM sleep is essential for memory consolidation. Sleep deprivation impairs hippocampal function. 7-9 hours of sleep per day is recommended.
Stress management: meditation and relaxation techniques reduce cortisol levels, which in excess damage the hippocampus. Spending time in nature and connecting with loved ones improves brain function.
Limiting stimulants: excessive alcohol consumption and chronic stress impair hippocampal neurogenesis.
What weakens the hippocampus
The hippocampus can weaken under the influence of various factors that negatively affect its structure and functioning. Here are the most important ones:
Chronic stress and high cortisol levels: long-term stress leads to excessive cortisol secretion, which damages hippocampal cells and inhibits neurogenesis. This can cause problems with memory, concentration and spatial orientation.
Lack of sleep: sleep, especially REM sleep, is crucial for the regeneration of neurons and memory consolidation. Sleep deprivation leads to the atrophy of neurons in the hippocampus and a decrease in cognitive abilities.
Unhealthy diet: a diet high in simple sugars and trans fats (fast food, processed foods) contributes to inflammation in the brain. A deficiency in omega-3 acids, antioxidants and B vitamins impairs neurogenesis.
Lack of physical activity: a sedentary lifestyle reduces blood flow to the brain, which limits the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the hippocampus.
Alcohol and drug abuse: alcohol damages hippocampal cells and impairs the formation of new neural connections. Drugs (e.g. cocaine, amphetamines) lead to neurotoxicity and memory impairment.
Chronic diseases: Alzheimer’s disease, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension can lead to hippocampal degeneration. Depression and other mental disorders can also negatively affect its functioning.
Social isolation and lack of mental stimulation: lack of social interaction and new cognitive challenges impairs the brain’s neuroplasticity. The hippocampus develops when we learn new things and are socially active.